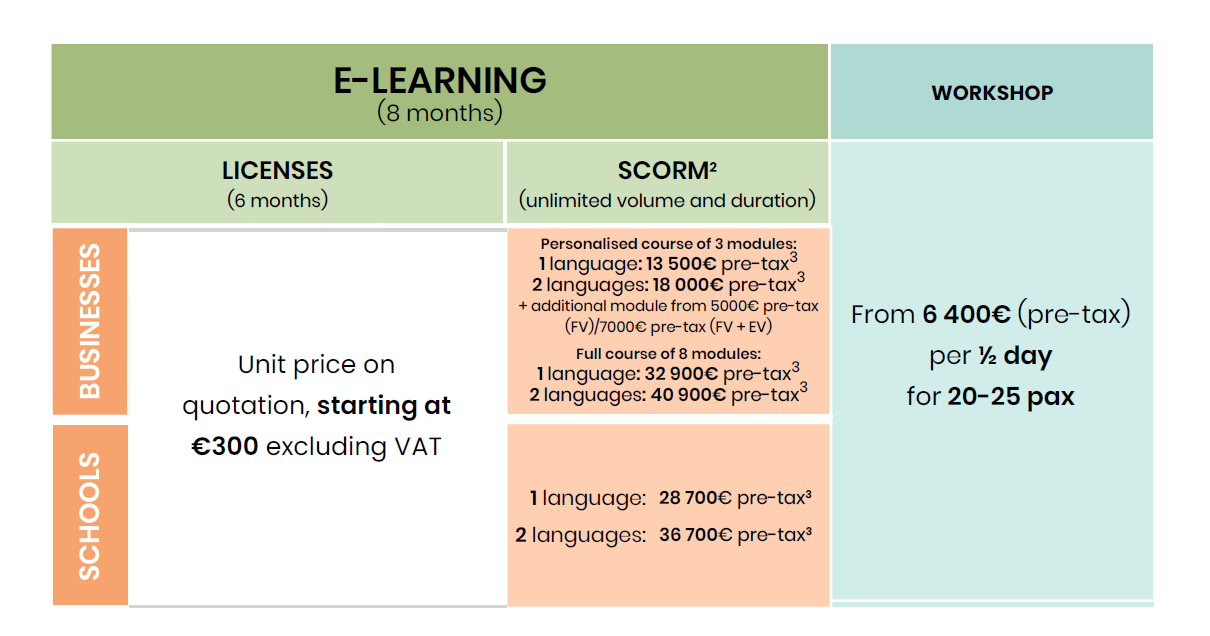
The training mechanism
This blended learning course includes:
- An e-learning course (available in French and English)
- Workshop
E-learning course
- 8 lessons 30 min each
- Online: Micro learning and adaptive learning
- Lessons are easy to understand thanks to a storytelling approach where the participant finds him-/herself in the shoes of a fictitious communicator
- Rich, varied, interactive content (facts and figures, inspiring strategies and campaigns, innovative ideas, quiz questions, smart habits to adopt)
- A memo sheet + tool sheets to download at the end of each module
- A multiple-choice quiz at the end of each module to validate the knowledge acquired
The 8 main topics are:
1) Responsible communication: how to move from a constraint to an opportunity?
The challenge of the module:
Understand the challenge of responsible communication for your brand, your company, and the increasingly preponderant role that communication has in the company's environmental and societal commitment. Help develop a point of view on the evolution of communication towards more responsibility, in the light of the current context and new regulations on advertising.
The educational objectives:
- Learn key facts and figures about social and environmental issues facing organisations
- Review (or learn) key language elements so you can talk about them
- Understand communication as a full-fledged industry that must, like all industries, achieve sustainable transformation, particularly with regard to the growing use of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Understand its role and influence on society and how it can be a powerful vector of the ecological transition, particularly with regard to the growing use of AI
- Get to know the recent evolution of the regulations in the field of responsible communication
- Paris Agreement
- Carbon footprint
- Earth's biocapacity
- Responsible communication pillars (ADEME)
- AI
- IPCC
- Responsible consumption
- UDM FAIRe Program / REPRESENTe Challenge
- “Climate and Resilience” Law
- Climate Contracts
- Nympheas Award
2) Why and how to design eco-socially responsible messages?
The challenge of the module:
Understand the environmental and social impacts of messages, discover trends, practices, and regulations as well as several initiatives and campaigns which messages contribute to the ecological and societal transition. Find inspiration through examples of responsible while creative and impactful advertising messages and ideas.
The educational objectives:
- Learn the key principles of eco-social design
- Identify the risks induced by non-responsible messages, particularly through the use of Artificial Intelligence (greenwashing and other types of washing, stereotypes, cognitive bias, over-consumption...)
- Conversely, be aware of the impact of the message in responsible communication
- Discover positive and inspiring campaigns from an environmental and/or societal point of view
- Understand the role of communicators in the creation of new narratives and collective social imaginaries in line with the ecological transition.
Examples of topics covered:
- ARPP/ Sustainable Development Recommendation
- Active Agencies CSR Label
- Greenwashing / social washing / Woke Washing
- Legal frameworks France / Europe
- New stories and collective imaginations
- Functionality economy
- Diversity, Inclusion, Stereotypes
- AI and bias
- Donut Theory
- Unstereotyped Alliance
3) How to produce a communication campaign responsibly?
The challenge of the module:
Understand the environmental impact of production and how to measure it; discover good eco-socio process practices in preparation (the key points to take into account to ensure responsible filming/shooting from the outset ), in production (the key points to take into account to ensure a smooth running of the shoot with a measured impact ), in post-production (the key points to take into account to ensure follow-up with reduced impact ), until the end of life campaigns (recycling, upcycling, donation, cleaning servers , etc.).
The educational objectives:
- Become aware of the environmental impacts of production
- Understand how to act from both an environmental and societal point of view throughout the production phase (pre-production and post-production included)
- Discover good practices and key tools for implementing eco-socially responsible production.
Examples of topics covered:
- Eco-socio production
- Ecological typos
- Responsible filming
- Carbon Calculation tool
- Carbon compensation/contribution
- The 5 Rs
- Life Cycle Analysis (LCA)
- Key players in France
4) How does responsible influence contribute to the progress of brands and businesses?
The challenge of the module:
Discover why and how influence – the main communication lever for organizations today – is becoming more and more regulated in France (and soon in Europe); Get aware and learn, through numerous business cases, the key principles of a responsible influence approach and the benefits that result from it.
The educational objectives:
- Discover the different influencers (content creators, Key Opinion Leaders, elected officials, journalists, etc.)
- Gain a better understanding of the current context, the regulatory framework and current solutions in place to counter the abuses of influence
- Understand the positive consequences from a social and/or environmental point of view of a responsible influence strategy
- Know the fundamental principles and appropriate behaviours of responsible influence.
Examples of topics covered:
- Grand Prix Strategies for Responsible influence 2023
- Macro vs micro influence
- Co-construction approach with stakeholders
- Responsible Influence Observatory & Certificate by ARPP
- Employer branding
- Communities
- Glassdoor
- Law June 9, 2023 on commercial influence
- REECH study
- E-label Responsible influence consultancy Agencies
5) How to organize responsible events?
The challenge of the module:
Identify the environmental and social impacts of your events, physical and hybrid; Discover how to organize more responsible events – from an environmental point of view – thanks to suitable solutions and tools – and from a societal point of view by favouring committed service providers and ensuring accessibility to all audiences.
The educational objectives:
- Learn the principles and key steps of responsible event planning
- Discover “responsible” events and actors committed to this approach
- Understand how to create and multiply the positive impact of my event
- Adopt the right reflexes, in particular the stakeholder evaluation process and the project impact measurement.
Examples of topics covered:
- Circular economy
- Waste management
- ISO 20121 standard
- Life Cycle Analysis – event
- Carbon offset
- Viva Technology 2024
- ADEME
- LEAD Label
- Accessibility
- Transportation
6) Digital technology : how to use it responsibly in communication?
The challenge of the module:
Understand the sources of “tech” pollution on the environment to better control them. Find out how to reduce the impact of its digital activities (material and energy sobriety, software eco-design, digital frugality, etc.) by better controlling design and its uses, and fighting against digital exclusion via e-accessibility; Become an actor in responsible digital technology through measured, responsible and fair use.
The educational objectives:
- Learn the key concepts and figures of the impact of digital technology on the environment
- Identify the stages of the digital life cycle where it is most important to act to preserve the environment
- Adopt the approach of digital frugality and sobriety in the design and use of digital technology
- Find out what digital accessibility is, how it applies and the opportunities it can offer.
Examples of topics covered:
- Environmental impacts of digital
- Digital eco-design/Digital sobriety
- Digital sustainability
- E-footprint tool – Publicis Sapient
- WEEE
- Evaluation and optimisation tools
- Responsible digital players
- Digital accessibility
- DSA and DMA
- REEN Act
7) What roles for the media in a responsible communication approach?
The challenge of the module:
Understand all the issues Media are facing, their responsibility and the plural and complex role they have to play today; Discover how they organise themselves both individually and collectively to address growing environmental and societal challenges as well as the solutions and tools they put in place.
The educational objectives:
- Become aware of the media's responsibility when it comes to their capacity to influence, as a counter-power and as an essential pillar of our democracy
- Understand the responsibility issues facing the entire media ecosystem
- Environmental impact
- Convenience and relationship with democracy
- Representations of the world
- Discover how players in the sector organise themselves and what they are doing to reduce their environmental footprint
- Adopt the reflex of involving stakeholders (agencies, media, consumers) to co-construct and test the solutions of tomorrow.
Examples of topics covered:
- Utility / Quality / Solidarity / Inclusivity
- Fight against disinformation (fake news)
- Law of July 7, 2023 (“digital majority”)
- Charter of Paris (AI and journalism)
- PEF method
- Common standards (AACC, SRI, UDM, UDECAM)
- Oneframe - UDM
- Global Media sustainability Framework/ GARM & Ad Net
- Solidarity advertising
8) Responsible Data: How to reconcile ethics, respect for the environment and user trust?
The challenge of the module:
Discover why data (and by extension Artificial Intelligence) has exploded in recent years and what are the economic, technological, political but also societal and environmental issues that it raises. Learn how to use it responsibly while putting it at the service of sustainability.
The educational objectives:
- Address the key figures and essential concepts concerning the ethical, societal and environmental issues around data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) that companies are up against
- Understand the context and the current regulatory environment on its use
- Understand the use of data and AI as a responsibility and an opportunity
- Identify its role and influence on business and society (individuals)
Examples of topics covered:
- Processing of personal data / Biometric data
- GDPR / CNIL
- Pact for climate-neutral data centres
- Responsible Data approach
- Responsible innovation
- Internal cookie/Third-party cookie
- Data Green Officer
- Ethics by design
- Artificial Intelligence/Generative AI
- AI Act
- Open data
Collective workshops aimed at taking action:
- From 3 hours
- Face-to-face and/or remote (Teams)
- Discuss the content seen in the e-learning course and identify the levers for action and avenues to be explored
- Apply the knowledge and tools, work on concrete cases, develop a roadmap to make it all effective
- Learn more about one or more specific areas of responsible communication with the help of experts